Introduction
Anesthesia; It is a state of analgesia and amnesia that occurs with the suppressed responses of the central nervous system (CNS) to painful stimuli.
Neuroleptanalgesia
It is analgesia performed by combining a narcotic analgesic drug (fentanyl) and a neuroleptic drug (dehydrobenzperidol, droperidol, haloperidol) by the IV route.
Neuroleptanesthesia
It is anesthesia created by adding nitrous oxide to the combination of neurolept analgesia.
Since these combinations are dopamine receptor blockers, their use in patients with Parkinson's is contraindicated.
Neurolept Analgesia: Fentanyl + Dreperidol
Neurolept Anesthesia: Fentanyl + Dreperidol + Nitrous oxide
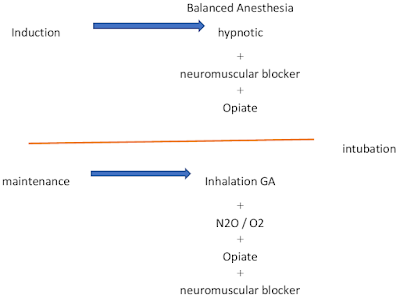
Balanced Anesthesia
It is a combination of nitrous oxide + a narcotic (Fentanyl) + Thiopental + Neuromuscular blocker.
• ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) determined the risk of anesthesia according to the physical condition of the patients.
|
ASA 1 |
A healthy person who does not have a disease or
systemic problem other than a normal surgical pathology that does not cause
systemic disorders. |
|
ASA 2 |
Person with a mild systemic disorder due to a
cause requiring surgical intervention or another disease |
|
ASA 3 |
A person with a disease (such as hypovolemia,
previous infarction, advanced diabetes) that limits his activity but does not
leave him weak |
|
ASA 4 |
A person with life-threatening (shock,
decompensated heart and respiratory failure, kidney failure) who completely
loses his strength |
|
ASA 5 |
Person in a state of death, who is not expected
to live more than 24 hours, whether or not he has surgery, who undergoes
surgical intervention as the last hope |
|
ASA 6 |
Patients with brain death whose organs were
removed for the purpose of donation |
|
E |
If the operation is urgent, the letter E is
written after the physical state. |
Potential Risk Factors for Perioperative Pulmonary Complications
Patient Factors
• Advanced age
• Smoking
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary
• disease Obesity
• Obstructive sleep apnea
Surgical Factors
• Incisions close to the diaphragm (such as thoracic, upper abdominal procedures, abdominal aortic aneurysm repair)
• Long-running transactions
• General anesthesia (relative to regional)
Summary of Fasting Guidelines as Pulmonary Aspiration Prophylaxis
Item Received ...... ...................... ........ ........... ........................ Minimum Fasting Time (hours)
Clear liquids (water, carbonated drinks, tea, coffee) ------------------------------- 2
Breast milk--------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
Baby food------------------------------------------------ -------------------------------- 6
Milk other than breast milk------------------------------------------------------------ 6
Light meal (toast clear liquids) ------------------------------------------------------- 6
Heavy food (oily foods) --------------------------------------------------------------- 8
Premedication
It is the preparation of patients for the operation using drugs.
Purposes of premedication: Eliminating anxiety, reducing secretions, reducing various autonomic reflex responses, providing amnesia, providing analgesia, sedation, antiemetic effect, reducing anesthetic requirement by reducing metabolic activity, facilitating anesthesia induction, reducing gastric fluid volume and increased pH, To provide prevention of allergic reactions, to relieve excitement before regional anesthesia, to increase the local anesthetic effect, special conditions (transdermal nitroglycerin in angina).
Drugs used in premedication
Antiemetics
Anticholinergics; atropine, scopolamine
H1 histamine antagonists; cyclizine, diphenhydramine, promethazine
dopamine antagonist; phenothiazine, butyrophenone, metoclopramide
sedatives and hypnotics
• Butyrophenones; pentobarbital, secobarbital
• Antihistamines; diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine. Chloral derivatives; triclophos Na, chlorhydrate
tranquilizers
Butyrphenones; haloperidol, droperidol
Phenothiazines; chlorpromazine, promethazine, promazine
Benzodiazepines; diazepam, nitrazepam, temazepam
Narcotic analgesics
Morphine, dolantin, fentanyl, buprenorphine
Anticholinergics
Atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate
